The global economy heavily relies on the shipping industry, which carries about 90% of global trade. However, this sector also contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and water and noise pollution. Therefore, environmental sustainability is a priority. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has set ambitious targets to reduce carbon emissions per transport work by at least 40% by 2030 and 70% by 2050 compared to 2008 figures. Digital technologies have immense potential to help achieve these targets and decarbonize the shipping industry.
Why is sustainability vital for the shipping industry?
Being one of the largest emitters of greenhouse gases in the world, the shipping industry has to mitigate its impact on the environment. Given its scale and reach, the sector has a huge potential to help achieve the objectives outlined in the fight against climate change, as mentioned in the Paris agreement.
Furthermore, adopting sustainable practices is not only about reducing the sea transportation industry’s carbon footprint but also about staying ahead of the curve and continuously improving its competitiveness in a constantly evolving market. These practices allow the development of innovative solutions that benefit both the industry and the environment.
In other respects, going green contributes to cutting costs and ensuring the sector’s economic viability in the long run by:
- Increasing energy efficiency;
- Reducing waste;
- Ensuring compliance with stricter regulations implemented by governments around the world to avoid penalties and fines;
- Meeting the ever-growing demand from consumers and stakeholders for commitment to social responsibility and allowing companies to enhance their reputation.
- Minimizing environmental risks.
That is the reason why, since the adoption of the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL) on 2 November 1973, ship-source has been a major concern for the maritime industry as a whole. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) created the Marine Environment Protection Committee (MEPC) in 1973. This entity placed under the authority of the United Nations London-based organization is dedicated to addressing environmental issues.
What are the benefits of environmentally friendly technologies for the shipping industry?

Digital technologies are instrumental in the effort to decarbonize the shipping industry, as they offer significant ways to lower its carbon footprint and mitigate the pollution it produces while decreasing reliance on traditional fossil fuels. Some short-term measures can bring significant improvement for existing vessels, but some very promising solutions will take time to fully unleash their potential.
Here are the key ways in which these technologies contribute to achieving the ambitious objectives set.
Suggesting the best routes for lower fuel consumption and carbon emissions
Shipping companies have to find the most fuel-efficient and low-carbon routes for their vessels. To take the best decisions, they rely on digital fleet management systems that function with real-time data on weather, sea conditions, traffic, vessel speed and performance, fuel consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions, among other factors. Multiple technologies help them in this regard:
- Internet of things and ships onboard navigation systems to capture and transmit data on the go to a centralized platform.
- Mobile satellite communication, such as the solutions provided by Inmarsat ensures seamless connectivity across the globe.
- Big data analyze this vast amount of information received, coupled with historical data provided by specialized suppliers such as Sinay. Its portfolio includes Metocean Data Analysis, which enables the simulation of unlimited scenarios to understand weather patterns and prepare for complex operations at a specific location.
On a wider scale, for all other stakeholders, data collection and analysis help identify areas for improvement and optimize operations, leading to less GHG emissions and increased efficiency.
Allowing carbon tracking and reporting
Digital platforms help shipping companies set targets for carbon emissions reduction, track progress towards meeting those goals, and report them. These platforms also provide transparency to customers and stakeholders about the company’s sustainability performance. This is even more important that starting in January 2023, a major regulatory change is in force regarding carbon emissions. It becomes mandatory for all existing ships to measure their Energy Efficiency Existing Ship Index (EEXI) as part of each ship’s yearly carbon intensity indicator (CII) evaluation. These new regulations are aimed at encouraging the adoption of more sustainable and energy-efficient practices throughout the shipping industry.
Allowing remote smart maintenance
Digital technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and machine learning algorithms enable remote monitoring of ship systems, reducing the need for physical inspections and maintenance. Shipping companies can therefore maintain their vessels’ equipment more efficiently. This contributes to mitigating fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions from ships’ auxiliary engines, preventing breakdowns and delays to decrease costly idle time and respect the schedule.
Facilitating the transition and efficient use of alternative fuels
Switching to alternative fuels, such as hydrogen, natural gas LNG, ammonia, or biofuels, has become imperative for ship designers and owners. Digital technologies, including simulation tools, digital twin technology, and data analytics, are used to evaluate the feasibility and potential performance enhancement that can be achieved through the adoption of low-carbon energy sources for propulsion.

Giving access to renewable energy sources via smart grids
Smart grids are advanced energy systems that use digital technologies to manage the generation, distribution, and consumption of energy. Ships can connect to the grid and access renewable energy sources. The vessels equipped with the necessary technology could use wind turbines or solar panels to generate power that they can then feed back into the smart grid, where it can be distributed to other ships or even back to shore.
Promoting the development of autonomous ships
Autonomous and electric ships powered by renewable energy sources could drastically cut down carbon emissions from the shipping industry. Digital technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning have the potential to facilitate the development and implementation of autonomous vessels, making shipping more energy-efficient and sustainable.
Reducing pollution from ships
Ballast water treatment technologies are effective in preventing the spread of invasive non-native species, which can occur due to the discharge of water taken up from one location to stabilize ships during transit. The such measure protects local ecosystems from devastating ecological consequences.
Waste heat recovery is another technology that contributes positively to the shipping industry’s decarbonization efforts. It works by capturing the waste heat produced by a ship’s engines and using it to generate electricity or power auxiliary equipment. This helps reduce the amount of fuel needed to power the vessel, leading to lower harmful gas and improved energy efficiency.
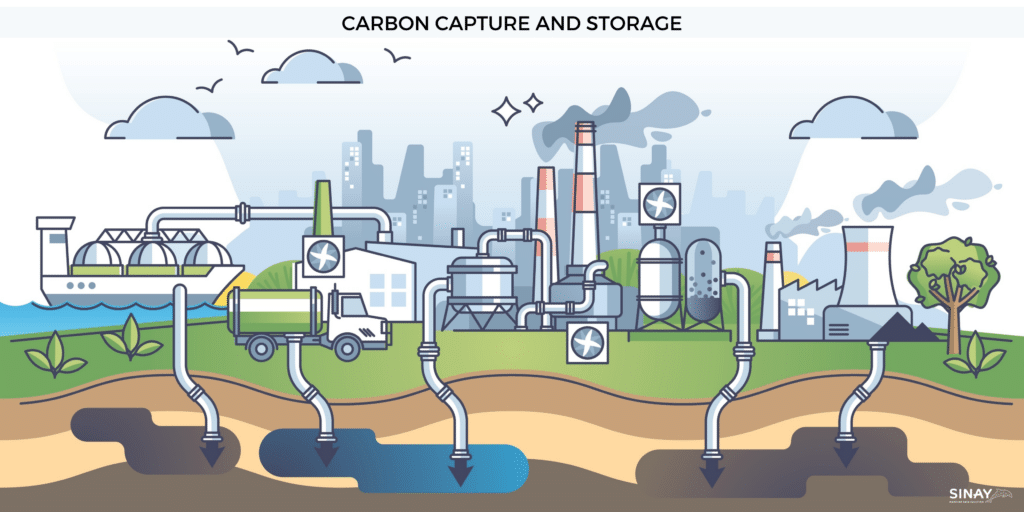
Storing carbon to diminish carbon emissions
On existing ships, the use of carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology could significantly help ship owners and operators minimize their environmental impact and help ensure compliance with increasingly strict emissions regulations, to avoid penalties. This CCS process involves capturing carbon dioxide emissions from ships before they are released into the atmosphere with exhaust gas, and then storing them in a secure location, such as underground or beneath the ocean floor. Already used in other industries, such as power generation, this solution has not yet been widely adopted in the maritime industry. This is partly due to space constraints that make it difficult to install the necessary equipment on board. However, some experts are optimistic that innovative design solutions could overcome these challenges and make carbon capture and storage a feasible option for existing ships.
How does the collaboration of all stakeholders facilitate the decarbonization of the industry?
By embracing these technologies, ships can improve their energy efficiency and reduce their reliance on traditional fossil fuels, ultimately leading to a greener and more sustainable future.
However, while technology undoubtedly offers many advantages, it cannot single-handedly drive the major transformation that the maritime industry needs. Decarbonization of this highly interconnected and interdependent system is a complex and multi-faceted issue problem, considering the sector’s global reach and the extent of the task. No single stakeholder can have all the answers or resources for the transition to a low-carbon shipping industry.
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions from shipping is a shared responsibility and the success depends on the active involvement of all stakeholders within this global network, including:
- international and national regulatory bodies led by the IMO, as well as policymakers;
- local authorities (governments, port authorities…);
- shipowners, vessels designers and builders, carriers and shipping agents, port operators, marine contractors; logistics providers and their associations;
- technology developers. For example, Sinay develops artificial intelligence-based APIs that are specifically designed to assist maritime innovators in developing powerful tailored tools for various purposes: GHG emissions monitoring, vessel tracking and ETA calculation, air/water quality monitoring, underwater acoustics assessment, etc.
- energy suppliers, who develop alternative fuels;
- shippers and beneficial cargo owners (BCO);
- experts and classification societies, such as the Norway-based company DNV, which acts as a trusted consultant for the maritime industry. It provides digital solutions for managing risk and improving safety, delivers certification, and provides technical advisory services for various assets: ships, pipelines, processing plants, offshore structures, electric grids, etc.
In addition to regulators, other entities are involved in developing transport policies to address the challenges posed by global transformations. For instance, the International Transport Forum, an intergovernmental organization of the OECD with 64 member countries, serves as a think tank for the transportation sector, including the ocean carriage of goods.
Likewise, the Global Maritime Forum reunites leaders from the maritime community, policymakers, NGOs, experts, and other decision-makers from around the world. This non-profit organization aims at enhancing sustainable long-term economic development by shaping the future of the global sea transportation trade. To achieve its objectives, The Forum members discuss common challenges and promote joint projects and initiatives that can drive sustainable change and long-term impact.
Coordinated action from all those parties leverages the collective knowledge, expertise, and resources to develop innovative solutions and implement global standards and regulations while avoiding duplication or waste of efforts. This is crucial to tackling the obstacles and embracing the upcoming possibilities associated with the decarbonization of the shipping industry.
Conclusion
The incorporation of digital technologies within the shipping industry has the potential to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions and enhance operational efficiency. Nevertheless, all stakeholders across various countries and regions must collaborate towards a common goal and be at the same level.
Frequently Asked Questions about using digital technologies to decarbonize
The IMO has set targets to reduce carbon emissions per transport work by at least 40% by 2030 and 70% by 2050 compared to 2008 figures.
The shipping industry is one of the largest emitters of greenhouse gases in the world, and mitigating its impact on the environment is crucial. Adopting sustainable practices is also important for the industry’s competitiveness, cost-cutting, and economic viability in the long run.
Environmentally friendly technologies such as digital platforms, data analysis, and IoT sensors enable the shipping industry to lower its carbon footprint, reduce fuel consumption, and mitigate the pollution. They also facilitate the adoption of low-carbon energy sources for propulsion and allow for remote maintenance.
Digital fleet management systems that function with real-time data on weather, sea conditions, traffic, vessel speed and performance, fuel consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions, among other factors. Internet of things and ship on-board navigation systems, mobile satellite communication, and big data analytics are also instrumental in this regard.
Starting in January 2023, it becomes mandatory for all existing ships to measure their Energy Efficiency Existing Ship Index (EEXI) as part of each ship’s yearly carbon intensity indicator (CII) evaluation. Digital platforms help shipping companies set targets for carbon emissions reduction, track progress towards meeting those goals, and report them. These platforms also provide transparency to customers and stakeholders about the company’s sustainability performance.
Focus on data to make effective decisions
Discover our modules
Environmental Monitoring
Monitor air quality in real-time, be alerted when a threshold is reached & easily comply with regulation thanks to the automated reports.
Monitor water quality in real-time, predict and avoid water pollution & comply with regulations thanks to the automated reports.
Deliver a preliminary metocean analysis and the associated report in jut a few minutes.
You may also be interested by those others environment application :





